Botox, brand name, is botulinum toxin A which is a protein in nature. The Bacteria (clostridium botulinum, C. butyricum, C. baratii and C. argentinense) produce this protein that is also responsible for botulism disease. Botulinum toxin has several therapeutic uses. An example may include, muscle spasms, cervical dystonia, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, migraine headaches as well for cosmetic purposes. For common people, cosmetic uses are known to reduce or lessen wrinkles in the face, which is a normal process of aging.
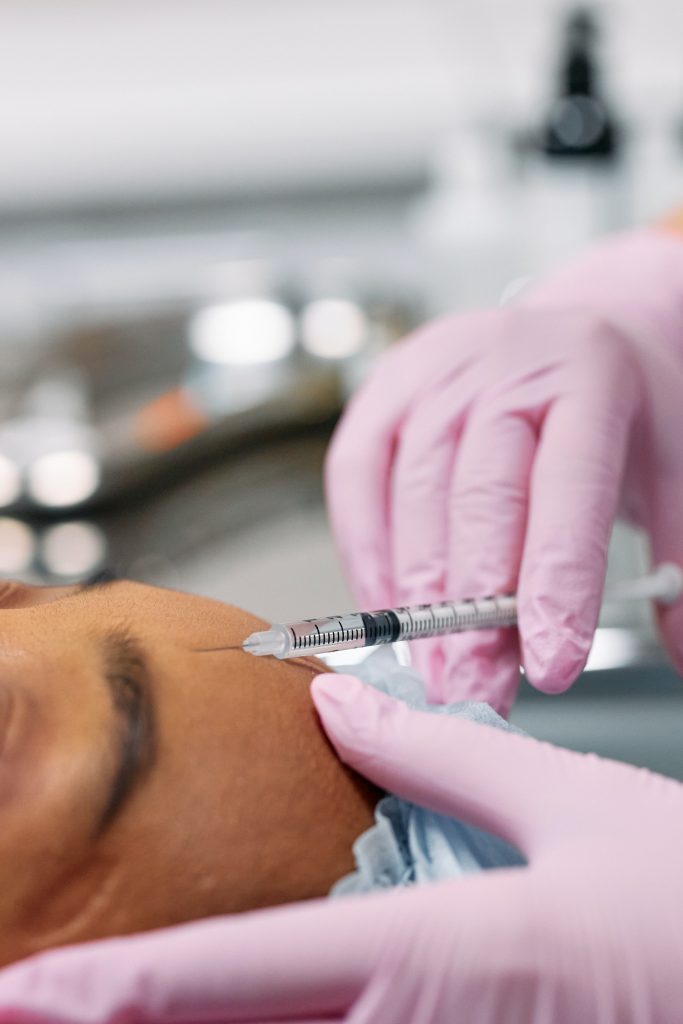
Moreover, most individuals who are not associated with the medical profession think that it is only for cosmetic purposes like anti-aging or anti-wrinkle medication to reduce facial wrinkles.
Nature of Botox and background
Botox or botulinum toxin is a lethal naturally occurring toxin. But it can be used as a powerful and highly effective medication for various medical conditions and for cosmetic purposes. Its importance was found around1950s. The scientists discovered that injection of a minute quantity of botulinum toxin type-A in muscles, particularly in overactive muscles. This may result in decreased muscle activity and weakness, which can last up to 3-4 months.
Botulinum toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine. This is a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction and is released from its stores in neurons and causes muscle weakness.
Cosmetic uses:
it is most commonly used for cosmetic purposes. In the United States alone, approximately 5 million cosmetic procedures are done using it every year. In the US, the persons who can see Botox and persons eligible to do the cosmetic procedure using Botox vary from State to State. Persons who provide Botox cosmetic procedures include plastic surgeons, dermatologists, dentists, aesthetic spa physicians, etc.
For cosmetic purposes, a small quantity of botulinum toxin is injected into the skin, which causes paralysis of facial muscles (other muscles are not affected) and prevents the development of wrinkles on the face.
Treatment of Botox:
- Cervical dystonia, also known as spasmodic torticollis.
- Strabismus (Squint), excessive blinking (a problem known as blepharospasm).
- Excessive axillary sweating (hyperhidrosis) and excessive sweating. USFDA approves this treatment.
- Migraine (especially severe form) and other headaches. The results of this treatment are conflicting.
- Focal neuropathies are sometimes helpful with local intradermal injection of Botox.
There are also other medical conditions used but are not approved by USFDA and most other government authorities. Some doctors use them although they are not approved. These include:
- Anal fissures, and spasms of the vaginal muscles.
- Dystonia of jaw, face, limbs, etc. Pain in temporomandibular joint (jaw joint).
- Incontinence due to neurogenic bladder, painful bladder syndrome.
- Diabetic neuropathy wound healing.
- BHP (benign hyperplasia of the prostate gland).
- Dysfunction of the vocal cord due to dystonia.
- The problem of movement due to diseases of CNS such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinsonism, cerebral palsy, etc.
- Detrusor muscle overactivity.
- Chronic musculoskeletal pain.
Side effects
Side effects due to the proteinous nature
The toxicity of botulinum toxin in humans is very low, due to the use of minute quantities for medicinal and cosmetic purposes. There are several side effects of Botox, although most of them are temporary and minor in nature. The side effects are mainly due to the proteinaceous nature of the product and its mechanism of action of it. Side effects are mainly of two categories, namely allergic reaction (due to the proteinaceous nature of Botox) and paralysis of the wrong muscle along with the desired muscle paralysis (due to the mechanism of action).
Side effects are due to its proteinaceous nature:
They are mainly allergic manifestations because allergic manifestation is caused by antigens, which are proteins in nature.
Side effects of Botox due to its mechanism of action:
Botulinum toxin acts by inhibiting the release of the physiological neurotransmitter acetylcholine from its stored vesicles in the neurons. Due to a lack of acetylcholine muscle paralysis occurs, as acetylcholine is required for the contraction of muscles.
The side effects occur due to the effect of Botox on the wrong muscles and overexpression of pharmacological action. For example injection of Botox in the face may cause paralysis of muscles of eyelids and result in drooping of eyelids and inability to close eyes. Paralysis of muscles on one side may result in an asymmetrical smile.
Injection of Botox in the jaw muscle (masseter muscle) may result in loss or reduction of power to chew.
Other side effects of Botox:
There are also some side effects that are not related to Botox, such as bruising at the site of injection. In cosmetic use bruising may result in drooping of eyelids, inability to close eyes, diplopia (double vision), asymmetric smile, etc. With appropriate precaution (application of pressure to the injection site) bruising can be reduced to a great extent. Generally bruising lasts for one to two weeks but sometimes may last up to 6 weeks.
Botox may also cause flu-like syndromes, headaches, dry mouth, blurring of vision, difficulty in swallowing, redness, and swelling at the injection site.
There are some reports of death due to the use of Botox, although none of them are due to cosmetic use. The deaths were due to the spread of Botox to areas distant from the site of the injection for the treatment of various ailments and with see of various dose ranges.
——————————————————————
For a better experience with web hosting and domain, please click here
